Build Your First AI Agent in n8n: A Step-by-Step Guide
If you can use ChatGPT, you can build an AI agent. This comprehensive guide will walk you through creating your first AI agent from scratch using the n8n platform.
By the end, you'll understand how to give your agent a brain, connect it to tools like Google Sheets, and teach it exactly when and how to use those tools.
Watch it in action
Resources
- OpenAI API platform - For creating API keys
- ChatGPT prompt template for system messages (see below)
- My Notion Command Center system
Understanding AI Agents: The Foundation
Think of an AI agent as having three essential components that mirror human anatomy.
- First, there's the brain, composed of a chat model and memory.
- Second, there are tools like Slack, Google Sheets, and Notion that allow the agent to take action in the real world.
- Third, there's the brainstem in the form of a system prompt.
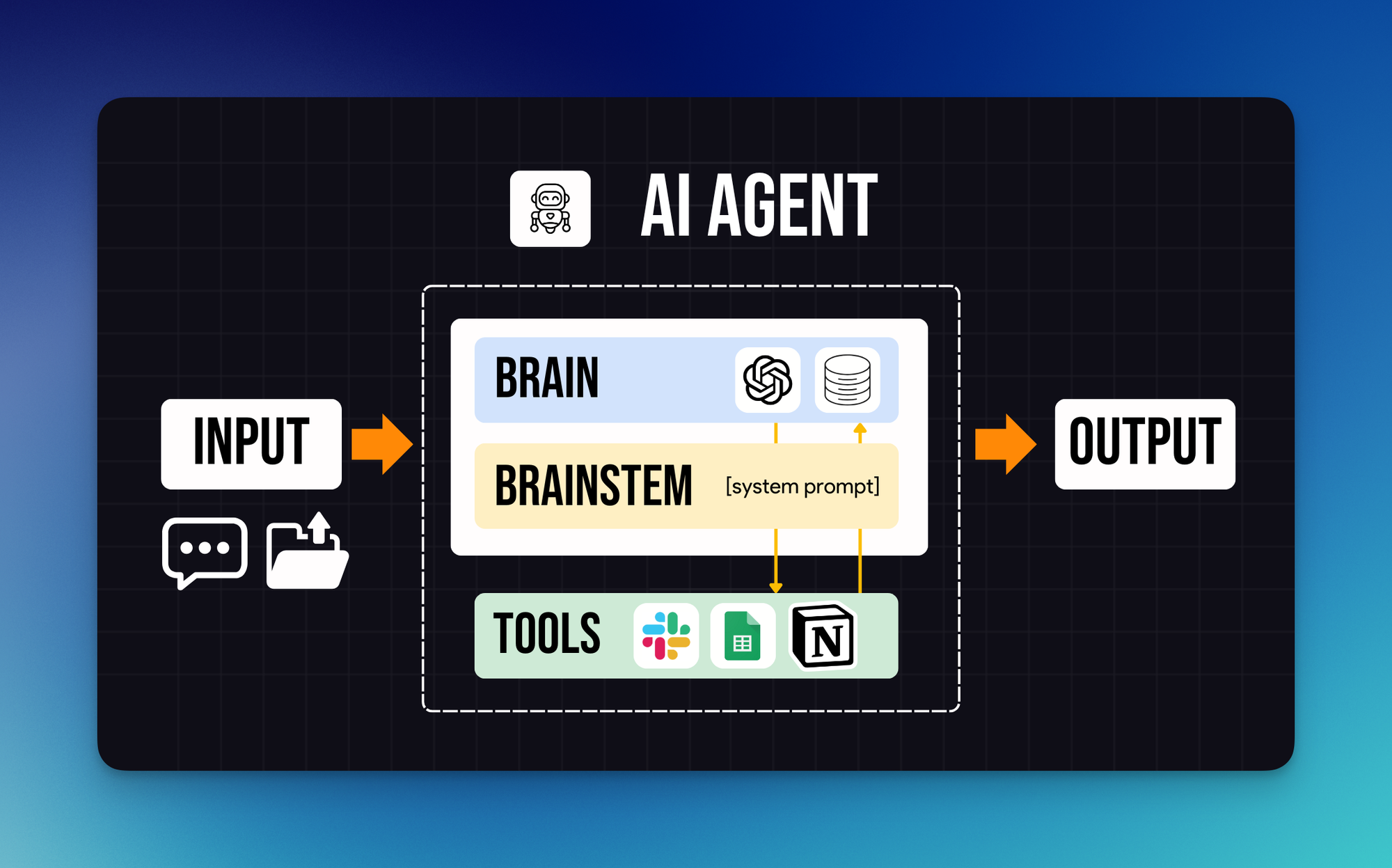
Just as the human brainstem relays information from the brain to the rest of the body, the system prompt performs a similar function by helping the agent brain control the tools correctly.
Getting Started with n8n
The agent we're building today will track subscription expenses in Google Sheets. When you type something like "I just subscribed to n8n for 20 euros a month," the agent will process your natural language input, confirm the details with you, and automatically add a properly formatted row to your subscription tracker spreadsheet with columns for Expense, Charge Date, Cadence, Cost, and Status.
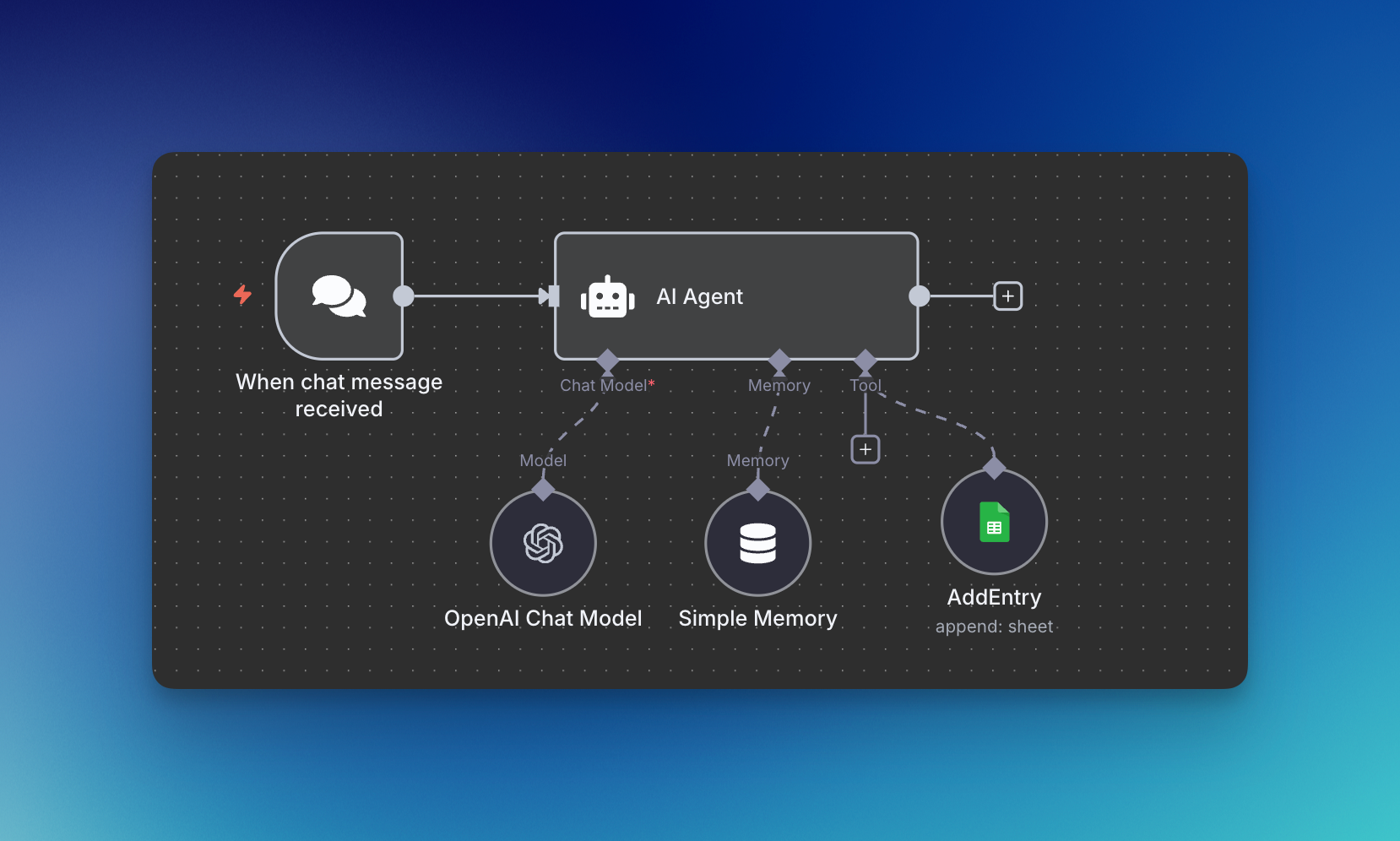
Step 1: Building the Brain
Creating the brain of your AI agent starts with establishing how you'll communicate with it. In n8n, begin by creating a new workflow and adding a chat trigger. This chat interface allows you to send messages to your agent in natural language.
Next, connect an AI Agent node to your chat trigger. Think of this connection like a relay race – the chat trigger passes your message to the AI Agent, which then needs to process it. The AI Agent node might look intimidating at first, but it's simply showing you what it receives (your chat input) and what it needs to process.
Adding the Chat Model
Your AI agent needs a chat model to think and respond. Connect an OpenAI chat model to your AI Agent node. If this is your first time, you'll need to create API credentials:
- Head to the OpenAI platform and create an account
- Navigate to Settings > Billing and add payment credits (this is separate from ChatGPT subscriptions – API usage is pay-as-you-go)
- Generate an API key under API Keys
- Copy and paste this key into n8n's credential field
For model selection, the latest mini models strike an excellent balance between cost and performance. These models are powerful enough for most tasks while keeping API costs manageable.
The Critical Role of Memory
Here's where things get interesting. Without memory, your AI agent suffers from permanent amnesia.
- Try telling an agent without memory "Hey, there's a list called the E List. Keep that in mind." When you later ask "What's the list called again?" it won't have any recollection of your previous message.
Adding Simple Memory solves this problem. Set the Context Window Length to 14 messages – this means if you send messages twice daily, your agent will still remember Monday's conversation on Sunday. This continuity transforms your agent from a goldfish into a helpful assistant that maintains context across interactions.
Step 2: Connecting the Tools
Tools give your AI agent the ability to interact with external services. For our subscription tracker, we'll connect Google Sheets as our primary tool.
Preparing Your Google Sheet
Before connecting the tool, create a new Google Sheet with these columns:
- Expense
- Charge Date
- Cadence
- Cost
- Status
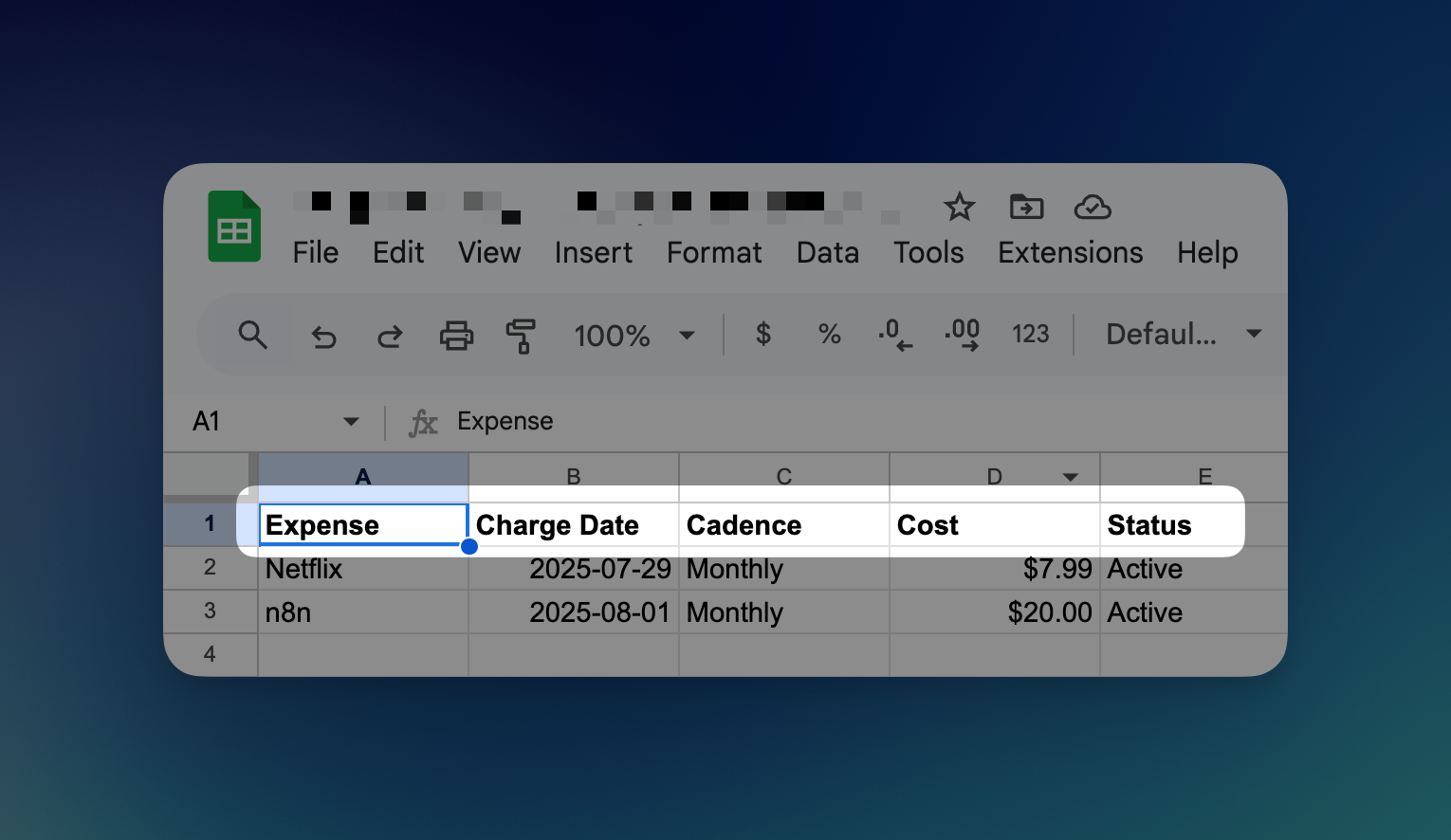
Name the tab "tracker" and keep this window open – you'll need the URL shortly.
Configuring the Google Sheets Tool
Back in n8n, add a Google Sheets tool to your AI Agent. The connection process is straightforward:
- Click "Sign into Google" and authorize n8n to access your Google account
- Set the operation to "Append Row" since we're adding new entries
- Select your document by URL and paste your Google Sheet's URL
- Choose the "tracker" tab from the dropdown
- Map the columns but let AI determine the values – click the sparkle icon for each field
Rename this tool to "AddEntry" for clarity. This naming convention becomes important when we write the system prompt, as we'll need to reference this specific tool by name.
Step 3: Activating the Brainstem
The system prompt is where the magic happens. It's the instruction manual that tells your AI agent how to use its brain and tools effectively. Without a proper system prompt, your agent has all the capabilities but no direction.
Generating Your System Prompt
Writing system prompts can be daunting, but here's a powerful shortcut:
- Take a screenshot of your n8n workflow
- Download the workflow as a JSON file (click the three dots menu > Download)
- Head to ChatGPT with the latest reasoning model
- Upload both files and ask it to generate a comprehensive system prompt for your subscription tracking agent
Prompt to Generate System Prompt
## TASK ##
Your task is to output a clear, precise, and comprehensive system message for my n8n AI agent designed to keep track of my subscriptions (i.e. recurring expenses).
## CONTEXT ##
The AI Agent is connected to a Google Sheet and has access to the "AddEntry" tool.
When the user sends a message like "I just subscribed to ChatGPT for 20 usd a month" the AI agent should first confirm its understanding then fill out the columns in the Google Sheet.
For example:
Expense = ChatGPT
Charge Date = By default use today’s date (date chat was sent) unless stated otherwise
Cadence = Monthly
Cost = $20
Status = Active
I've attached a .json file and screenshot for you to reference.
ChatGPT will analyze your workflow structure and create detailed instructions that tell your agent exactly how to handle subscription data, when to use the AddEntry tool, and how to format the information correctly.
Dynamic Date Handling
One common issue you'll encounter is date accuracy. Your agent might guess the wrong date when processing entries. The solution involves making your system prompt dynamic.
In n8n, you can drag variables from the input context (like the actual date and time of your message) directly into the system prompt. This ensures your agent always uses the correct date instead of making assumptions.
Testing and Refinement
Once your agent is assembled, testing reveals its true capabilities. Type "I just subscribed to iCloud for 10 USD a month" and watch the process unfold. A well-configured agent will:
- Process your natural language input
- Confirm the details with you before taking action
- Add the entry to your Google Sheet with all fields properly formatted
If something goes wrong, you have two troubleshooting options:
- You can either take a screenshot and ask ChatGPT for an updated system prompt; or
- Manually edit the system prompt to fix specific issues. The manual approach gives you deeper understanding of how system prompts control agent behavior.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Considerations
Think about what you'd expect from a human assistant managing your subscription tracker. They should check for existing entries to avoid duplicates, right? This logic translates directly to your AI agent workflow.
To implement duplicate checking, you'd add another Google Sheets tool configured to "Get Row" to read existing entries first. Then, modify your AddEntry tool to "Append or Update Row" instead of just appending.
Most importantly, update your system prompt to reflect this new workflow: instruct the agent to check existing entries before making changes.
These enhancements demonstrate the flexibility of AI agents. Once you understand the building blocks, you can create increasingly sophisticated workflows that handle edge cases and provide more intelligent responses.
If you enjoyed this
Check out my comprehensive guide on leveraging Google Gemini for advanced automation workflows!